jQWidgets Mobile PhoneGap Application for iOS

In this tutorial you will learn how to create a simple mobile application that pinpoints an iOS device's location and shows it in a Google Maps instance situated in jqxTabs. You may also be interested in how to easily create the same application for Android, BlackBerry 10 or Windows Phone 8.
1. Prerequisites
There are some prerequisites you must meet before you start developing iOS applications:
- You need an Intel-based Mac computer with OS X;
- You need to install the iOS SDK. It is included in Xcode, which you can download from the Mac App Store. You will be able to test an app using the iOS emulator, which is included with Xcode.
- To test an app on a real iOS device, it needs to have at least iOS 5.x installed. Supported devices include all iPad models, iPhone 3GS and above, and iPod Touch 3rd Generation or later. To install apps onto a device, you must also be a member of Apple's iOS Developer Program.
2. Install Apache Cordova
Firstly, download Node.js from http://nodejs.org and install it. After the installation, make sure the directory
/usr/local/bin is in your $PATH. To check if the directory
is in your $PATH, open Terminal and type:
$ echo $PATH
This outputs a list of directory paths separated by colons (:). If you cannot find
/usr/local/bin there, add it by following these steps:
- Run the following command in Terminal:
$ sudo nano /etc/paths
- Enter your password, when prompted;
- Go to the bottom of the file, and enter the path you wish to add.
- Press ctrl+X to exit;
- Press Y to save the modified buffer.
To install Apache Cordova open Terminal and type:
$ sudo npm install -g cordova
3. Create a New App and Open It in Xcode
To create a new app, type in Terminal:
$ cordova create geoloc com.example.geoloc "GeoLoc"
Enter the newly created app directory by typing:
$ cd geoloc
Then add iOS support to the app:
$ cordova platform add ios$ cordova prepare
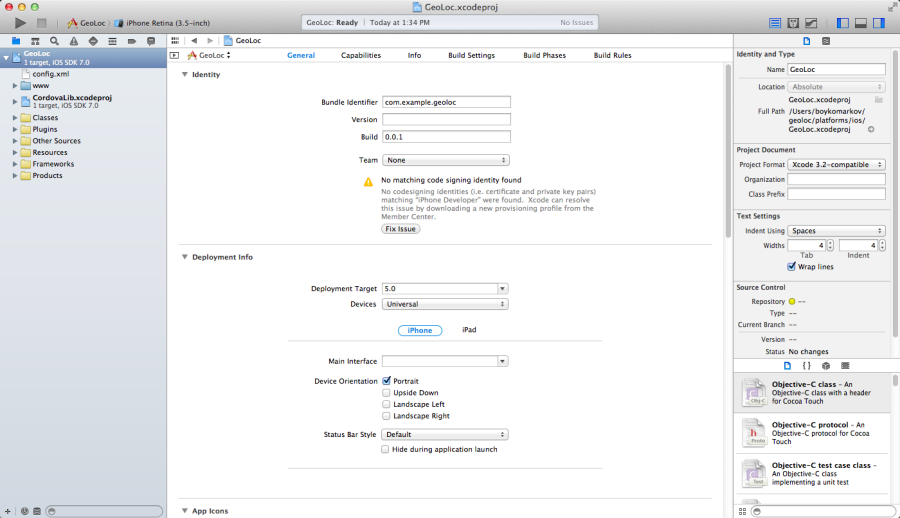
Go to the geoloc/platforms/ios folder and double-click the file GeoLoc.xcodeproj
to open it in Xcode. Yo will see the following screen:
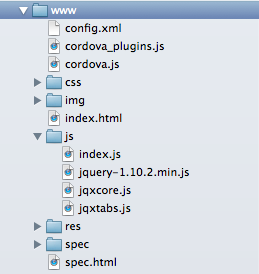
4. Modify the geoloc/platforms/ios/www Directory
We will now modify the files in the geoloc/platforms/ios/www directory
to achieve our desired functionality. Here is its contents after we have added all
the needed files:
Here is the source code of index.html in our example:
<!DOCTYPE html><!--Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under oneor more contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE filedistributed with this work for additional informationregarding copyright ownership. The ASF licenses this fileto you under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the"License"); you may not use this file except in compliancewith the License. You may obtain a copy of the License athttp://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing,software distributed under the License is distributed on an"AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANYKIND, either express or implied. See the License for thespecific language governing permissions and limitationsunder the License.--><html><head><meta charset="utf-8" /><meta name="format-detection" content="telephone=no" /><!-- WARNING: for iOS 7, remove the width=device-width and height=device-height attributes. See https://issues.apache.org/jira/browse/CB-4323 --><meta name="viewport" content="user-scalable=no, initial-scale=1, maximum-scale=1, minimum-scale=1, width=device-width, height=device-height, target-densitydpi=device-dpi" /><title>A jQWidgets mobile application, which demonstrates PhoneGap's Geolocation API.</title><link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="css/jqx.base.css" /><style type="text/css">.label{font-size: larger;font-weight: bold;}</style><script type="text/javascript" src="cordova.js"></script><script type="text/javascript" src="js/jquery-1.11.1.min.js"></script><script type="text/javascript" src="js/jqxcore.js"></script><script type="text/javascript" src="js/jqxtabs.js"></script><script type="text/javascript" src="js/index.js"></script><script type="text/javascript" src="https://maps.googleapis.com/maps/api/js?v=3.exp&sensor=true&libraries=places"></script><script type="text/javascript">$(document).ready(function () {app.initialize();});</script></head><body><div class="app"><div id="jqxTabs" style="margin-top: 25px;"><ul style='margin-left: 20px;'><li>Location Map</li><li>Location Details</li></ul><div><div id="map" style="width: 350px; height: 320px;"></div></div><div><div id="details"><span class="label">Latitude: </span><span id="latitude"></span>;<br /><span class="label">Longitude: </span><span id="longitude"></span>.</div></div></div></div></body></html>
There are references to the jQWidgets main CSS file (jqx.base.css), jQuery
and the jQWidgets files required for jqxTabs. The file index.js contains
the code of the app's functionality. The last script reference is to the Google
Maps API.
Note that the app's initialization code is called in a $(document).ready()
function to make sure that all local and external scripts have been properly loaded
before the application itself initializes.
And here is the contents of the file index.js:
/** Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one* or more contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file* distributed with this work for additional information* regarding copyright ownership. The ASF licenses this file* to you under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the* "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance* with the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at** http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0** Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing,* software distributed under the License is distributed on an* "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY* KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the* specific language governing permissions and limitations* under the License.*/var app = {// Application Constructorinitialize: function () {this.bindEvents();},// Bind Event Listeners//// Bind any events that are required on startup. Common events are:// 'load', 'deviceready', 'offline', and 'online'.bindEvents: function () {document.addEventListener('deviceready', this.onDeviceReady, false);},// deviceready Event Handler//// The scope of 'this' is the event. In order to call the 'receivedEvent'// function, we must explicity call 'app.receivedEvent(...);'onDeviceReady: function () {app.receivedEvent('deviceready');},// Update DOM on a Received EventreceivedEvent: function (id) {// create jqxtabs.$('#jqxTabs').jqxTabs({ width: 350, height: 350 });navigator.geolocation.getCurrentPosition(this.onSuccess, this.onError);},// successfully determined positiononSuccess: function (position) {$("body").append("Locaton set.<br />");var lat = position.coords.latitude;var lng = position.coords.longitude;$("#latitude").text(lat);$("#longitude").text(lng);$("body").append("Loading map...<br />");// initializes the mapvar myLocation = new google.maps.LatLng(lat, lng);map = new google.maps.Map(document.getElementById('map'), {mapTypeId: google.maps.MapTypeId.ROADMAP,center: myLocation,zoom: 15});$("body").append("Map loaded.");},// unsuccessfully determined positiononError: function (error) {alert(error.message);}};
Everything must be executed within the deviceready event handler, which
fires when Cordova has fully loaded. In the receivedEvent handler,
we initialize the tabs and pinpoint the device's location using the method geolocation.getCurrentPosition.
The callback function onSuccess is called when the location has been
successfully determined. The callback function onError is called when
there has been an error during location getting.
To enable Cordova's Geolocation API, we need to modify the file config.xml
by adding the following line:
<feature name="Geolocation"><param name="ios-package" value="CDVLocation" /></feature>
And here is the entire contents of config.xml:
<?xml version='1.0' encoding='utf-8'?><widget id="com.example.geoloc" version="0.0.1" xmlns="http://www.w3.org/ns/widgets" xmlns:cdv="http://cordova.apache.org/ns/1.0"><name>GeoLoc</name><description>A jQWidgets mobile application, which demonstrates PhoneGap's Geolocation API.</description><author email="dev@callback.apache.org" href="http://cordova.io">Apache Cordova Team</author><content src="index.html" /><feature name="Geolocation"><param name="ios-package" value="CDVLocation" /></feature><access origin="*" /><preference name="fullscreen" value="true" /><preference name="webviewbounce" value="true" /></widget>
5. Test the App
We are now ready to test the app. Click the Run button to view the app in the iOS emulator:
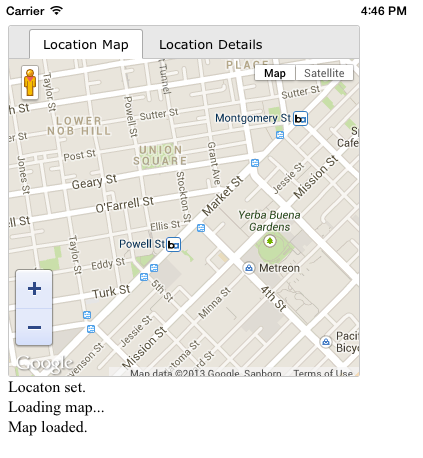
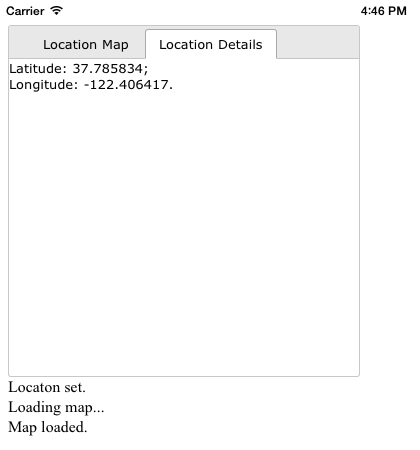
You can download the entire GeoLoc project here.